(external) caribous eat lichen fungus, and other tundra plants. (external) caribous eat lichen fungus, and other tundra plants.

Migration and hibernation are examples of behavioral adaptations used by animals in the arctic tundra.
Arctic tundra animals adaptations. Up to 24% cash back examples of structural adaptations of animals in the arctic tundra include: One physical adaptation of this animal has to do with its hoofed feet. Arctic wolves hunt musk oxen, caribou and arctic hares.
Polar bears are the largest creatures that inhabit the tundra. What adaptations do animals in the tundra have? Animals need shelter and insulation in the tundra.
Hibernation is a combination of behavioral and physical adaptations. When the weather starts to get cold migrating animals fly or swim to a warmer place where they can find food. The animals here tend to have thicker and warmer feathers and fur.
Animals have many adaptations to survive in this harsh environment. Some plants in the tundra such as the diamond leaf willow have an physiological adaptation in which they use their leaves to provide nutrients and protection. Numerous tundra animals hibernate to conserve energy during the long winters.
The arctic tundra plants and animals have to adapt themselves in order to survive the harsh conditions of this region. The physical adaptations of a musk ox allow it to survive in the harsh climate of the arctic tundra. For example, caribous possess hooves that are large and spreading.
Arctic moss, arctic willow, caribou moss, labrador tea, arctic poppy, cotton grass, lichens and moss. Plant adaptations in the tundra as i mentioned, it is the tundra plant adaptations that help it survive where mother nature is the least nurturing. This fur is shed during summer to prevent overheating and is thicker during winter to provide the most warmth possible.
Up to 24% cash back plant and animal adaptation. They have strong legs and claws that help dig in the snow so they can make burrows. Arctic wolves are smaller and white in colour.
Plants in the tundra stay low to the ground so they don’t get hurt by the harsh cold winds. The animals here tend to have thicker and warmer feathers and fur. Migration and hibernation are examples of behavioral adaptations used by animals in the arctic tundra.
Many tundra animals, such as musk ox, have a thick, fur coat that has two layers of fur. Tundra animals must adapt to unpredictable seasons and extreme cold in order to survive. Animals need shelter and insulation in the tundra.
Tundra adaptations size and shape snow and avoid the most severe conditions of winter. Animals have many adaptations to survive in this harsh environment. Hibernation is a combination of behavioral and physical adaptations.
Then they hibernate, or sleep during the winter. Hibernation is a combination of behavioral and physical adaptations. Tundra hares are larger and have shorter ears than hares that live in hot environments.
Up to 24% cash back this adaptation is unique to its species, and while similarities may be found with other aquatic life, this ability is mostly only seen in the arctic moss. It is also physical adaptations. Migration and hibernation are examples of adaptations used by animals in the arctic tundra.
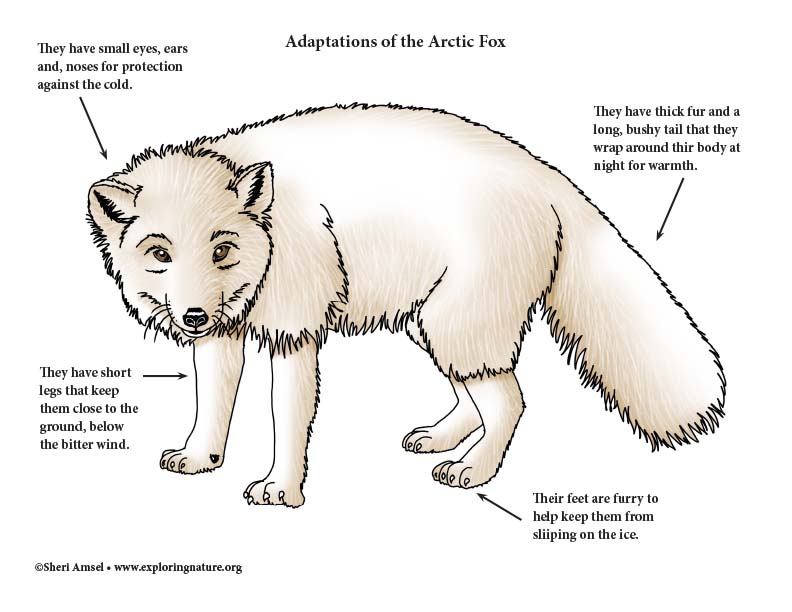
Lemmings have a lot of fur which protects and insulates them from the harsh weather. Arctic fox and ptarmigan, along with arctic hare and ermine, are camouflaged according to the season, changing from winter white to summer brown, and back again, each year. They have a thick undercoat of soft fur and an overcoat of long, thick hair.
Lemmings, arctic hares and arctic ground squirrels are a few animals that have adapted to the cold. Tundra plants are often dwarf relatives of similar plants There are two particular adaptations that help the lemming survive.
Many of them have larger bodies and shorter arms, legs and tails which helps them retain their heat better and prevent heat loss. Up to 24% cash back the lemmings have adaptations which makes it able to survive the harsh weather in the tundra. The siberian tundra, for example, is the coldest biome in the world.
Here are some animals that have. How do animals survive in the winter? The majority of animals that live in the tundra are migratory, and only visit for a portion of the year.
Their adaptations include having big paws to dig in the snow, and also white fur. They can be found near coasts. They also live in the tundra, which is a treeless region found in the arctic.
Animals of the arctic tundra have adapted to survive frigid conditions, according to the conservation institute. Animal adaptations migration and hibernation are examples of behavioral adaptations used by animals in the arctic tundra. Arctic animals use adaptations such as thick fur or feathers, having blubber under their skin, or making burrows to hide in.
Their concave hooves allow them to travel in snow conditions. Many of them have larger bodies and shorter arms, legs and tails which helps them retain their heat better and prevent heat loss. During the summer, brown bears behavior is to eat about anything they can find.
Tundra swans like to eat shell fish. The bear�s physical adaptation allows. The tundra is a cold, windy climate with little rainfall that is under a blanket of snow for most of the year.
A small surface area to volume ratio. Up to 24% cash back polar bears may eat reindeer, small rodents, fish, or berries. (external) caribous eat lichen fungus, and other tundra plants.
Shrews, the smallest of all mammals, thrive in the tundra. They use their tough hooves to break and dig through the ice to find grass and other vegetation. Up to 24% cash back migration and hibernation are examples of behavioral adaptations used by animals in the arctic tundra.
Arctic foxes have shorter ears than desert kit foxes. The conservation institute notes that there are a few common elements that tie many tundra animals together, such as heat retention in the body, trapped air. Wolves hunt in small packs.