Then the brown and collared lemmings, insects, and musk oxen eat the plants. They provide the energy for everything else.

The herbivores who eat plants and the carnivores who eat other consumers then they�re scavengers, who eat dead plants and animals arctic tundra food web the source producers decomposers
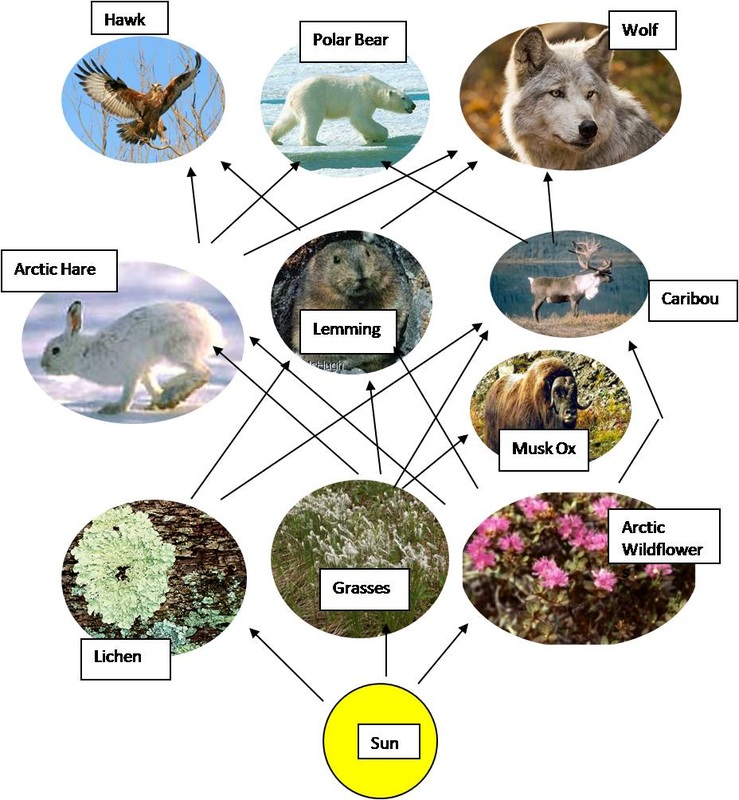
Arctic tundra animals food web. This food chain is part of a more complex food web involving producers and consumers (herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores). They provide the energy for everything else. Start the food web at the sun (start the ball of yarn there).
If we took the plants out of the ecosystem the. Herbivores eat plants, algae, and other producers. Have the student move to a photosynthesizing plant with the yarn, then to a herbivore, then to a carnivore.
The plants and animals of the arctic tundra interact over large areas to create a food web that helps all of its members survive the harsh conditions. There are more plants than any other living thing because they are the bottom of the food chain. Then the brown and collared lemmings, insects, and musk oxen eat the plants.
First the grasses, lichens, sedges and willows produce the energy. Food webs in the arctic tundra: Up to 24% cash back arctic tundra food web.
The arctic hare eats the arctic willow, which is also. Some of the consumers in the food webs are krill, fish, birds, reindeer, and seals. Copy of arctic food webs (in lesson materials) ball of yarn arctic tundra animals food web overview students learn about what type of polar animals live in the arctic.
The arctic tern eats the atlantic salmon which than eats the krill. The food web is missing a main component in the transfer of energy. That is some information about animals in the arctic
The herbivores include arctic hare, lemming, musk oxen, and caribou. The herbivores who eat plants and the carnivores who eat other consumers then they�re scavengers, who eat dead plants and animals arctic tundra food web the source producers decomposers What do animals eat in the tundra?
The primary consumers in the arctic tundra terrestrial food web are caribou, pika, arctic hare, musk ox and insects. The sun is the main source of energy, it gives off energy to the plants you see in the picture. A simple explanation of the food chain in the tundra region.
Alaska arctic tundra created by: Arctic fox reindeer arctic hare lemming musk ox lichen grass wildflower sun 1) list the producers, primary onsumers, secondary onsumers and tertiary onsumers. Krill are the major primary consumers, but some fish and tiny sea creatures, such as copepods, also eat phytoplankton.
The animals (insects, mice, chipmunks, squirrels, rabbits, deer) that mostly eat. The fragile food chains of tundra support some of the most amazing species on the planet, including the likes of gray wolves, polar bears, snowy owls, and arctic foxes. Some common tundra animals are reindeer, arctic foxes, snowy owls, musk oxen, and polar bears.
Plants start the food chain. Study examples of primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers in the tundra. They are at the second trophic level.
- limate change is having an impact on species. Lesson preparation prepare a picture sign for each of the organisms in the food web. Food web all animals on one sheet with arrows * food web all animals on one sheet without arrowsattention!
The marine arctic food web, like all other food webs, is made up of primary producers, consumers and decomposers. The food web is compiled for specific animals. They are at the third trophic.
Objectives students understand the relationships between various trophic levels within the arctic tundra. When light and temperature conditions of the tundra permit, plant growth begins. Organisms that break down and recycle waste and dead organisms.
Food web interactions as you can see, the food chain is as follows: This is a food web i created for the arctic tundra. The animals after the plants are herbivores they eat plants, so that is where herbivores get their energy.the animals after the herbivores are the carnivores, and the carnivores only eat meat.
The sun sends out enormous amounts of energy, which we need to live, in the form of light. Food web are caribou, pika, arctic hare, musk ox and insects. The example below shows the energy flow in a basic food chain in the tundra.
An example of an animal that is negatively affected by climate change is the polar bear. Producers here include grasses, lichens, and caribou moss. Help the students create the arctic food web.
The limited sun for photosynthesis of the polar tundra means growth of green plants is. Some examples from the tundra biome are the arctic wolf, caribou, and the polar bear. Up to 24% cash back food web of an arctic ecosystem the arctic seal is eaten by the polar bear and eats the atlantic salmon t he polar bear eats the atlantic salmon, and so does the arctic seal.
What animals live in the tundra +kids? Up to 24% cash back there are lots of animals including polar bears, arctic foxes, seals and many more in the arctic tundra and arctic. After the carnivores hunt and eat their prey, they eventually get old and die.
Herbivores that eat these plants include the musk ox, arctic hare, and lemmings. The animals food sources affect plants and other animals through the natural food chain keeping the population just right. A community of organisms that interact with each
Learn about the arctic food chain and see how it compares to the arctic food web. March 24, 2014 — image — leave a comment. Incorporate some death and decomposition with fungi and bacteria and create a giant food web of yarn and interrelationships.
Tundra food web clipart/ tundra food chain realistic clip art includes 11 files color+ 13 files black white png/jpg.you�ll get : For tundra plants and animals, survival is not just about battling the harsh environment of this biome, but is equally about being a part of its complex. Up to 24% cash back the plants include lichen, grasses, and arctic wildflower.
The carnivores include hawk, polar bear, and wolf. They are larger species that don�t reproduce as much.