
Each cell has a limiting boundary, the cell membrane, plasma membrane or plasmalemma. Some proteins are globular in shape whereas others are fibrous in nature.
The cell membrane, therefore, has two functions:
Cell membrane definition and function pdf. Cell membrane structure and function. Cell membrane (plasma membrane) the outer thin membrane or the layer of the living cell is known as the cell membrane. Extracellular matrix (ecm) only animal cells contain various protein fibers and complex carbohydrates function:
Regulates the entry of certain solutes and ions. It is a living membrane, outermost in animal cells but internal to cell wall in plant cells. Some proteins are globular in shape whereas others are fibrous in nature.
The term cell membrane was given by nageli and cramer (1885) for the membrane covering of the protoplast. Tails (fatty acids) are hydrophobic “water fearing” and directed inward 2. The cell’s organelles and its intracellular solutes (some inor ganic and some organic) are contained within the cell by its membrane.
Cell membrane two word definition: Some of the membrane proteins have carbohydrate parts attached to help cells in recognize each other and certain molecules. Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment function:
No cell wall, outermost structure is cell membrane or plasma. For example, haemoglobin is a globular protein, but collagen, found in our skin, is a fibrous However, in plants, bacteria and mushrooms, it is surrounded by a thickness cell.
- isolate cell’s contents from outside environment 2) regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3) communicate with other cells note:. Regulates what enters and leaves the cell (like a fence with gates) provides protection and support for the cell organelle: A typical plant cell wall is primarily composed of carbohydrates that are.
The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. Polar heads are hydrophilic “water loving” b. A 3d diagram of the cell membrane function of the cell membrane
It is also known as the plasma membrane in animal cells. In the plant cells, it is known as plasmalemma. It separates the cytoplasm (the contents of the cell) from the external environment.
The cell membrane plays an important role in regulating the entry and exit of specific substances within the cell. List 4 functions of the cell or plasma membrane: Also called the plasma membrane.
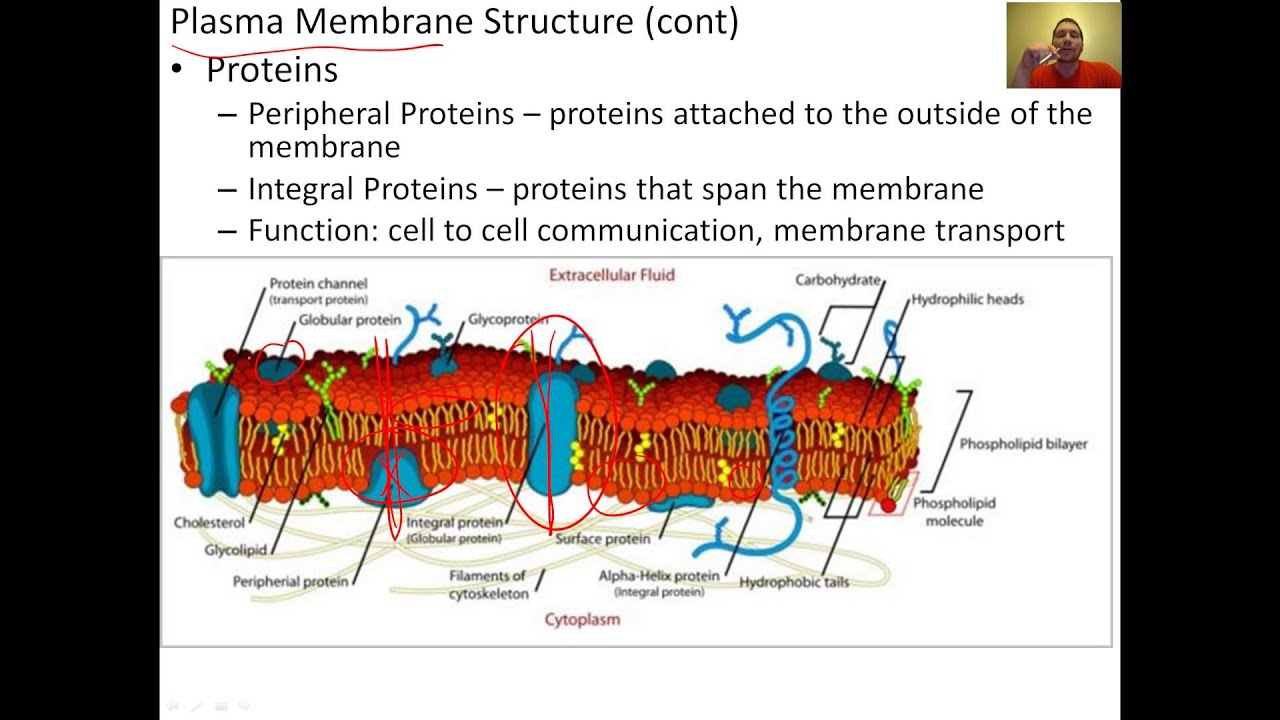
2 major populations of membrane proteins: It is sometimes referred to as an invisible surface layer because it is too thin to be visible with a light microscope. Components of the cell are enclosed in a membrane.
Acts as a barrier to protect the cell and a “doorway” letting substances in or out of the cell. Some of the functions of the cell membrane include protecting and enclosing the cell, giving shape to the cell, allowing transportation of materials in and out of the cell, and carry out metabolic reactions near the inner surface of the cell membrane. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell.
Can you guess, which part of the cell gives it shape? Plasma membrane structures * 1. First, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and, second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products.
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a physical barrier between a cell and the surrounding environment. The membrane separates cells from one another and also the cell from the surrounding medium. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment.
The cell membrane, therefore, has two functions: It is the most external part of the cell in animals. All cells have a plasma membrane which encloses the cell and allows interactions between the cell and its environment •the plasma membrane has three functions 1) isolates the cell’s internal contents from the external environment 2) regulates the flow of materials into and out of the cell 3) allows communication with other cells
The plasma membrane is porous and allows the helping to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body. Each cell has a limiting boundary, the cell membrane, plasma membrane or plasmalemma. Carbohydrate chains glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Membranes are mosaic of structure and function. Assists in communication between cells 3. It maintains the intracellular concentration of electro lytes and biologic compounds that is distinctly different from that of the extracellular fluid.
Integral proteinspenetrate the hydrophobic core of. Altough, all that contained inside the cell is not allowed to leave less permitted by the plasma membrane. The cell membrane regulates the transport of.
It is flexible and can fold in (as in food vacuoles of amoeba ) or fold out (as in the formation of pseudopodia of amoeba ) animal cell 1. Similar to our skeletal system. A membrane is a collage of different proteins embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer.
Separate s contents of cell from its surroundings. Helps the cell keep its shape and aids in organelle movement around the cell. Structural support correctly color code and identify the name for each part of the cell membrane.
Modelling the structure and function of the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane: It is a feature of all cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic. The membrane has limited and selective perme ability;
Cell membrane structure and function the cell membrane, cytoplasmic membrane or plasma membrane (a structural component of all living cells) is a living, dynamic layer that surrounds and limits the cell. Thin membrane that surrounds the cell. For instance, cell membrane keeps toxins from entering inside, while nutrients and essential minerals are transported across.
Cell membrane are proteins and lipids • membrane proteins and lipids are arranged in a particular fashion, both contributing to containing the cell and to selectively allowing or blocking the traffic of certain substances through the cell • such arrangement of molecules provides fluidity to the cell membrane