The cell membrane of the eukaryotic cell plays a major role in the diffusion and osmosis of cells. The plasma membrane is the outermost layer of the cell.
Major features of eukaryotic cells •eukaryotic cells contain organelles organelles:
Cell membrane function in eukaryotic cells. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its environment. The primary function of the eukaryotic cell membrane is to give the cell a specific shape. Some of the major functions of cell membrane of eukaryotic cell are as follows:
Eukaryotic cell function eukaryotic cells are cells that have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles. A eukaryotic cell has the following important features: It also protects the integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing certain substances in, while keeping other substances out.
It is often referred to as a fluid mosaic phospholipid bilayer that is hydrophilic externally and internally, but hydrophobic at. Free uk delivery on eligible orders cell walls: One is to transport nutrients into the cell and also to transport toxic substances out of the cell.
Eukaryotic plasma membrane eukaryotic cells are delimited by the cytoplasmic membrane and contain cytoplasm, ribosomes and dna. Most prokaryotic cells have a rigid cell wall that surrounds the plasma membrane and gives shape to the organism. It also contains locomotory organs such as cilia and flagella.
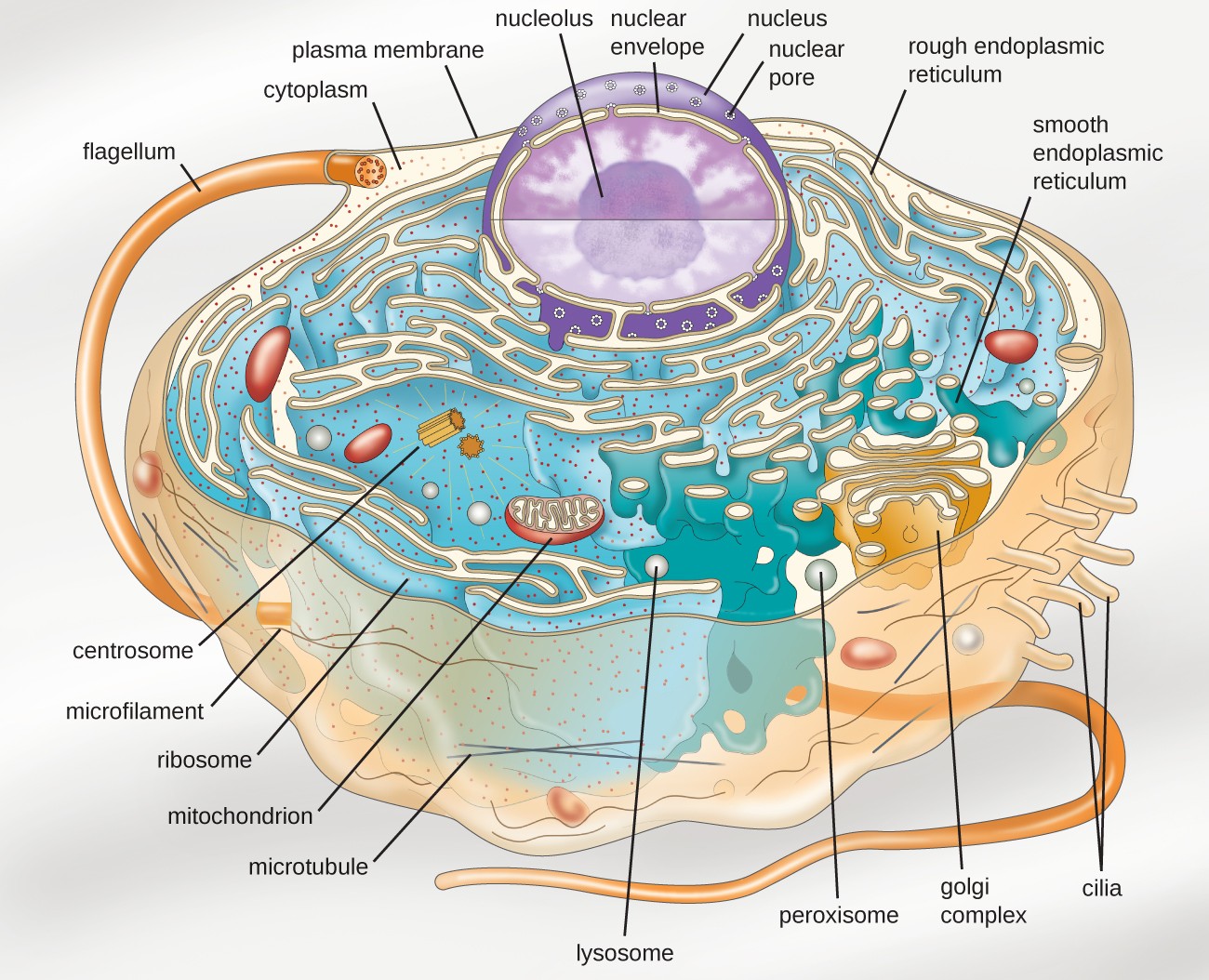
Major features of eukaryotic cells •eukaryotic cells contain organelles organelles: There are various cell organelles, out of which, some are common in most types of cells like cell membranes, nucleus, and cytoplasm. In eukaryotic cells, the membrane that surrounds the nucleus — commonly called the nuclear envelope — partitions this dna from the cell’s protein synthesis machinery, which is located in the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotes need membranous organelles in order to compartmentalize the various functions of the cell. It also provides a fixed environment inside the cell, and that membrane has several different functions. However, some organelles are specific to one particular type of cell.
Where is the cell membrane in a eukaryotic cell? Is cell membrane prokaryotic or eukaryotic. By holding the organelles in place the eukaryotic cell is able to facilitate transport.
Biological membranes have three main functions. A eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane. The nucleus has a dna that carries all the genetic information.
Eukaryotic cells, organelles are often enclosed by their own membrane.analogous to the body�s internal organs, organelles are specialized and perform valuable functions.q1. It includes the nucleus, the endoplasmic reticulum, and vesicles, the golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles/vesicles. The cell membrane of the eukaryotic cell plays a major role in the diffusion and osmosis of cells.
(2) they are receptors and channels that enable specific molecules such as ions, nutrients, waste products, and metabolites that mediate cells and extracellular activities that pass between organelles and organelles. The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell. Cell organelles are specialized entities present inside a particular type of cell that performs a specific function.
Describe the characteristics of eukaryotic cells. Plasma membrane is important in eukaryotic cell and it has many internal compartments. The plasma membrane is the inner layer of the cell envelope and its main function is to selectively allow the ions and organic molecules through it in and out, and regulate the movement of substances in and out of cells.
(1) keep toxic substances away from cells. The plasma membrane is the outermost layer of the cell. These cells make up the bodies of all multicellular organisms, such as plants and animals.
It has mitochondria, golgi bodies, cell wall. The endomembrane system ( endo = within) is a group of membranes and organelles (figure 4) in eukaryotic cells that work together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. In summary, membranes play a vital role in the function of organelles in eukaryotic cells, their inherent properties tailoring specific membranes to carry out a diverse range of tasks in various organelles.
Cellular recognition and adhesion 4. Eukaryotes also need fibrous cytoskeletal components to hold the cell in place. Recall that dna contains the information required to build cellular proteins.
Once again, the properties of these membranes directly influence their ability to perform critical functions within the eukaryotic cell.
