It is also known as the plasma membrane in animal cells. Cell membranes | function, structure, model, facts & notes.

Thin membranes bound all living cells and many of the tiny organelles internal to cells.
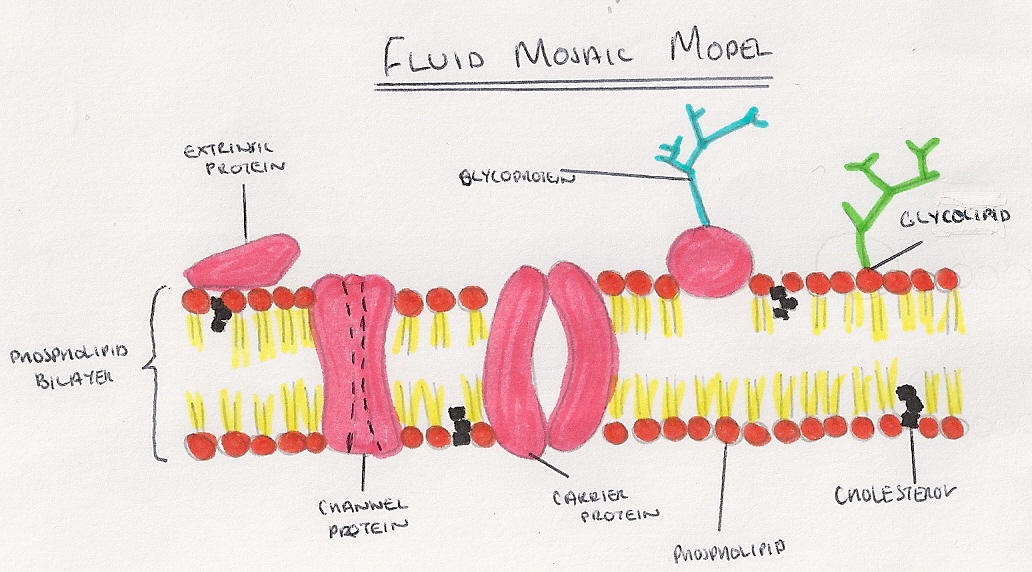
Cell membrane structure and function a level. Cell membrane is a protective covering that acts as a barrier between the inner and outer environment of a cell (in animals). It is also known as the plasma membrane in animal cells. Cell membrane overview and fluid mosaic model (opens a modal) fluid mosaic model:
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles while protecting the cell from its surrounding. The plasma membrane (also known as the cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of a cell from its outside environment. For comparison, human red blood cells, visible via light microscopy, are.
The cell surface membrane creates an enclosed space separating the internal cell environment from the external environment, and intracellular membranes form compartments within the cell such as the nucleus, mitochondria and rer. Up to 24% cash back membrane structure: It also works as a container for cell organelles.
The exact mix or ratio of proteins and lipids can vary depending on the function of a specific cell. The cell membrane has a bilayer structure made of. Over the past several decades, the efforts of biochemists, cell and molecular biologists, and hematologists have provided an appreciation of the complexity of rbc membrane structure, while studies of the rbc membrane disorders have offered.
Cell membrane structure and function chapter 5. This organelle is also referred to as plasma membrane. Cell membranes | function, structure, model, facts & notes.
Learn the structure of the plasma membrane, which makes up both cell surface membranes and organelle membranes. You just studied 14 terms! Thin membranes bound all living cells and many of the tiny organelles internal to cells.
Level up on all the skills in this unit. 1) isolate cell’s contents from outside environment 2) regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3) communicate with other cells note: The cell membrane or plasma membrane (or cytoplasmic) is the one that surrounds the cell.
Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment function: It represents the boundary between the intracellular environment and the extracellular environment. The term cell membrane was given by nageli and cramer (1885) for the membrane covering of the protoplast.
Membranes do not only separate different areas but also control the exchange of material. The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cell�s cytoplasm. A plasma membrane forms the barrier between the cell cytoplasm and the extracellular environment.
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that protects the cell and separates it from its environment. The cell membrane, therefore, has two functions: Learn the components (phospholipids, cholest.
Images obtained through electron micrography reveal the bilayer structure of cell membranes. If so, then check out this � membrane structure and function quiz� that is given below. All membranes in a cell have the same basic structure, which compartmentalises organelles from its external environment.
Formed from a phospholipid bilayer, with the hydrophobic tails pointing towards each other, and the hydrophilic heads pointing outwards. It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cell�s shape. First, to be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cell in and unwanted substances out and, second, to be a gate allowing transport into the cell of essential nutrients and movement from the cell of waste products.
Membranes are vital structures found in all cells. Cell signalling is when cells communicate with one another by signals. Cell membrane (plasma membrane) the outer thin membrane or the layer of the living cell is known as the cell membrane.
Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane. The fluid mosaic model describes the structure of the plasma membrane as a mosaic of components —including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates—that gives the membrane a fluid character. It serves as a barrier that mediates between the cell and the environment that surrounds it.
Cell membrane structure and function. In plant cells, the membrane encapsulates the protoplasm. Cell membrane are proteins and lipids • membrane proteins and lipids are arranged in a particular fashion, both contributing to containing the cell and to selectively allowing or blocking the traffic of certain substances through the cell • such arrangement of molecules provides fluidity.
Plasma membranes range from 5 to 10 nm in thickness. It is a fluid mosaic of lipids, proteins and carbohydrate. They cross the membrane only through transmembrane.
The cell membrane, therefore, has two key functions: It is the outermost part of the cell in animals. In the plant cells, it is known as plasmalemma.
(d) describe the roles of components of the cell membrane: Legend (opens a modal) possible mastery points. They act as a barrier between the cell and its environment/ the organelles and the cytoplasm.
To be a barrier keeping the constituents of the cells in and unwanted.