The form and properties of the molecules determine their functions. Membranes divide the cell into compartments where different chemical cellular activities can take place.

Tails (fatty acids) are hydrophobic “water fearing” and directed inward 2.
Cell membrane structure and function ppt. Plant cell plant cells have different structures contains: Cell membrane structure and function. Tails (fatty acids) are hydrophobic “water fearing” and directed inward 2.
Structure & function of cell membrane. It is the control centre of the cell. Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins • phospholipids are the most abundant.
8 characteristics that all living things share consist of organized parts (cells). The phospholipid bilayer the plasma membrane is common to all cells separates: The membrane’s lipids and proteins can move laterally within the bilayer.
The cell is the basic unit of structure and function. W o r k t o g e t h e r recap cell parts, such as cell membranes, are made up of biological molecules. Extracellular matrix (ecm) only animal cells contain various protein fibers and complex carbohydrates function:
The plasma membrane the gateway to the cell photograph of a cell membrane cell membrane the cell membrane is flexible and allows a unicellular. Regulates what enters and leaves animal cell cell (plasma). Largest cell organelle present in eukaryotic cells it is usually spherical it has double layer nuclear membrane with nuclear pores it has transparent granular matrix called nucleoplasm , chromatin network composed of dna and histone proteins it also has a spherical body called nucleolu s function:
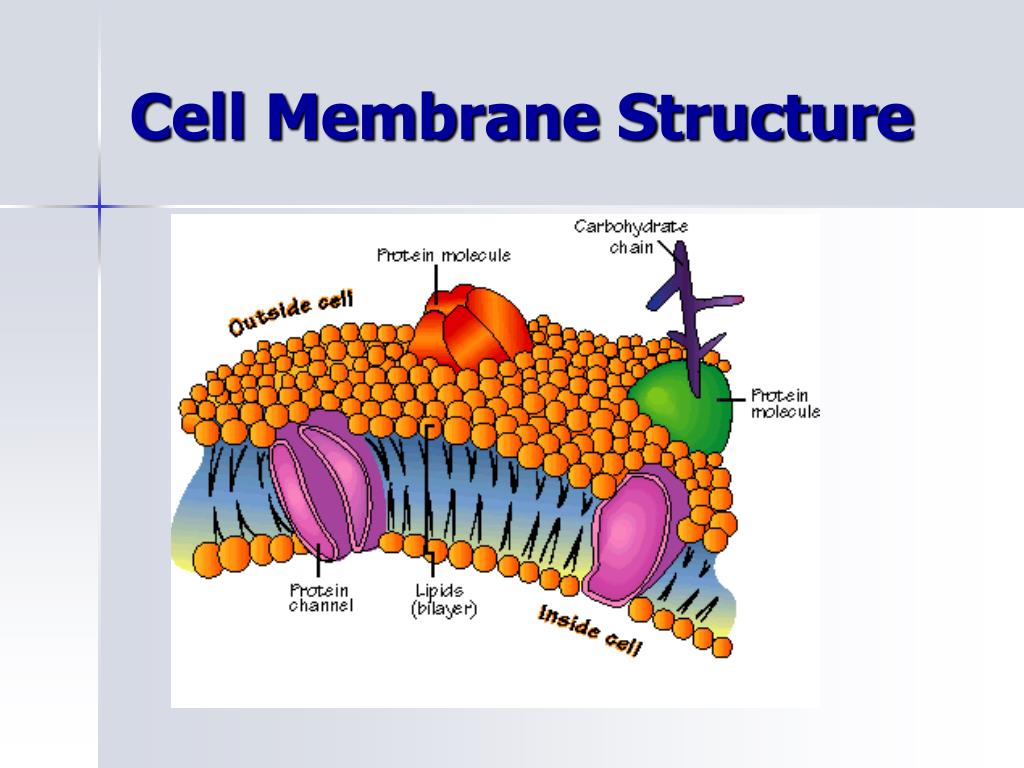
Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. Mosaic = made of many different molecules (lipids, proteins, carbohydrates) cell membrane animation * predict the two reasons things can’t directly go through the membrane: Cell membrane structure and function.
Cell membrane are proteins and lipids • membrane proteins and lipids are arranged in a particular fashion, both contributing to containing the cell and to selectively allowing or blocking the traffic of certain substances through the cell • such arrangement of molecules provides fluidity. Cell wall great wall of china chloroplast site of photosynthesis vacuole (large central, takes up most part of cell) cell membrane regulates substances in and out of the cell. Polar heads are hydrophilic “water loving” b.
Membranes divide the cell into compartments where different chemical cellular activities can take place. The plasma membrane or the cell membrane is a thin, biological membrane present in all eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells that forms a boundary between the cell and its environment and regulating the flow of materials in to and out of cell. A soap bubble consists of a thin, flexible _____.
Allows substances in an out. The structure and function of the cell membrane ppt notes cells function similarly in all living organisms the cell membrane is kind of like a soap bubble. Osmosis is a kind of diffusion.
The cell membrane is a fluid mosaic model. The bilayer behaves like a fluid more than a solid. Plasma membrane structures * 1.
The structure and function of the cell membrane components of the cell membrane: The plasma membrane is the outer boundary of the cell and is selectively permeable it contltrols the flow of subtbstances itinto or out of the cell. The teacher should introduce the essential question and the standard that is aligned to the essential question.
Likewise the cell membrane is a thin, flexible layer that seals the inside of the cell from its outside environment. External surface lined with hydrophilic polar heads cytoplasmic surface lined. Assists in communication between cells 3.
Vesicles may combine with plasma membrane to secrete contents lysosomes contain digestive enzymes functions aid in cell renewal break down old cell parts digests invaders vacuoles membrane bound storage sacs more common in plants than animals contents water food wastes mitochondria break down fuel molecules (cellular respiration) glucose. Selectively permeable size (duh) polarity (from last unit) *. Carbohydrate chains glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Internal living cytoplasmic from external environment of cell phospholipid bilayer: | powerpoint ppt presentation | free to view cell transport: 1) isolate cell’s contents from outside environment 2) regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3) communicate with other cells note:
Cell membranes actively and passively control what materials enter and leave the cell. Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment function: The soapy membrane _____ the ins ide air from the outside.
The cells maintain an approprite amount of all molecules within them to. Fluid = pliable/easily moved b. Life at the edge • the plasma membrane is the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings • the plasma membrane exhibits selective permeability , allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others.
Summarize what makes osmosis a special type of diffusion. The form and properties of the molecules determine their functions.