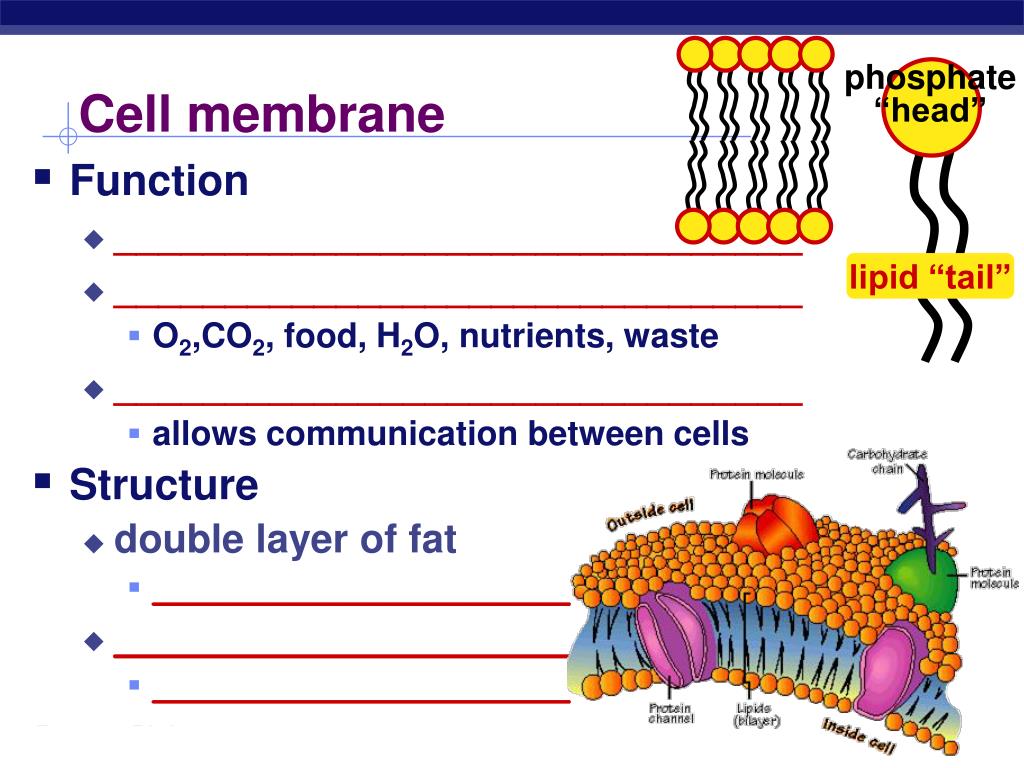
Match the general functions with the correct type of organic compound 1 cell membrane structure: Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that are essential for several biological functions, ranging from energy storage to cell signaling.

Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier, allowing some dissolved substances, or solutes, to pass while blocking others.
Cell membrane structure energy storage. Match the general functions with the correct type of organic compound: Fluid mosaic structure of biological membranes.docx. Lipids make up protective barriers.
Describe each cell organelle and its function. Describe the molecular components of atp. The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cell�s cytoplasm.
Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane. Functions match the general functions with the correct type of organic compound. It begins with a look at the chemical reaction that produces soap and then examines the chemical composition of a wide variety of lipid types.
And the same here, philip is a lipid bi layer because it has two layers of hopefully pits a in in the cell membrane. The nucleoid is a unique prokaryotic structure consisting of the cell’s aggregated dna. Ribosomes and proteins take most of.
Properties and functions of lipids are. The primary role of carbohydrates is to supply energy to all cells in the body. Design, modification and characterization of durable catalyst nanostructure design, construction and tunnel control of proton exchange membrane currently, the proton exchange membrane is.
Cell membrane structure, energy storage: How do adp and p relate to atp and energy generation and energy. Provides long term energy storage, provides insulation, and provides protection.
It is flexible to change the shape as needed. Okay, this is not to get in answer the option for this question because for example, in the cell membrane in my undies are forceful lipids. Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier, allowing some dissolved substances, or solutes, to pass while blocking others.
What is the difference between the nuclear envelop and the cell membrane in terms of structure and function? Major features of eukaryotic cells •mitochondria extract energy from food molecules, and chloroplasts capture solar energy. Storage granules are simple small organelles, bounded by a lipid bilayer membrane.
Outside is the cell envelope (cell membrane plus cell wall) and other external structures attached to the envelope. Glucose enzymes, transporters, structural components: It is usually located in the central part of the cell and contains the bulk of the organism’s genome.
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Cell membrane structure and function •the fluid phospholipid bilayer helps to isolate the cell’s contents Energy source , energy storage , cell membrane structural components , hormones , vitamins , vitamins absorption , protection , insulation.
Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that are essential for several biological functions, ranging from energy storage to cell signaling. The cell wall is 0.1 μm to several μm in thickness. How does this relate to maternal genetics?
Co 2, h 2o, o 2) (figure 4.3a) rate depends on: On the inside of the membrane, it contains the stored material. It is a thin and delicate structure.
This module explores the world of lipids, a class of compounds produced by both plants and animals. •cell structures that have a specific function and are surrounded by a. Different materials may be stored for different purposes by storage granules depending upon the location where they are found.
They comprise cell membranes and some of the structure of cell walls in plants. What do carbohydrates do in the cell? It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cell�s shape.
Lipids play several roles in organisms. It uses water and sunlight to pump out hydrogen without need of high heat or pressure. The exact mix or ratio of proteins and lipids can vary depending on the function of a specific cell.
It is the thick and rigid structure with a fixed shape. Quite often, lipids function alongside proteins. Membrane structure and function types of movement across membranes:
Membrane carbohydrates perform two main functions: Glucose and glycogen are examples of a group of organic compounds called: The motion turns light energy into a cellular fuel.
Which organelle has its own dna? Lipids provide energy storage to plants and animals. Storage, structural lipids & others.
Plant vacuole •plants have large central vacuoles that store water and These granules are surrounded by a lipid bilayer and are composed mostly of phosphorus and oxygen. Plants and other natural systems use energy to move protons across a cell membrane.
Start studying cell membrane test. The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible, the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells. Structure explains how the molecules are made and functions, how they work.
Pay off for facts in a cell membrane and finally a structure. Match the general functions with the correct type of organic compound 1 cell membrane structure: