Thin membranes bound all living cells and many of the tiny organelles internal to cells. We all keep in mind that the human body is very elaborate and a technique.
Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities.
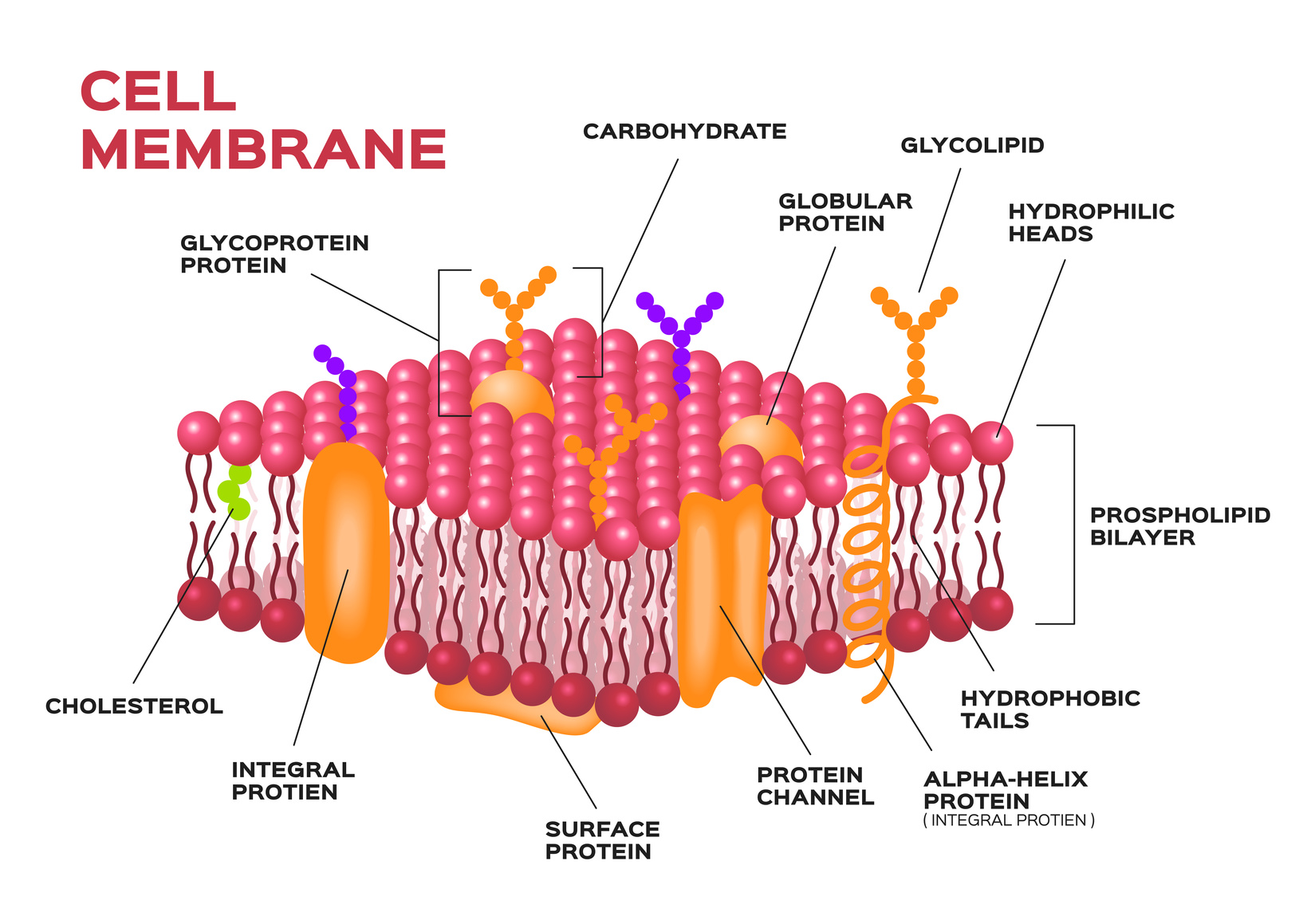
Cell membrane structure labeled. Anatomical closeup drawing with cross section element. Carbohydrate, globular protein or cholesterol location visualization. Scanning electron micrograph (sem) of adipocytes (ad) membrane structure and function prokaryotic cells:
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Double layer of phospholipids • hydrophilic ends form outer border • hydrophobic tails form inner layer • lipid tails of phospholipids are unsaturated (c = c) chapter 4: Structure a is a _____.
Because the bacteria cell structure lacks a nuclear membrane, they are group as prokaryotic cells different from the cells with nuclear membranes known as eukaryotic cells. It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cell�s shape. The bilayer structure is attributable to the special.
There are no organelles in the prokaryotic cells, i.e., they have no internal membrane systems. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable. The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cell�s cytoplasm.
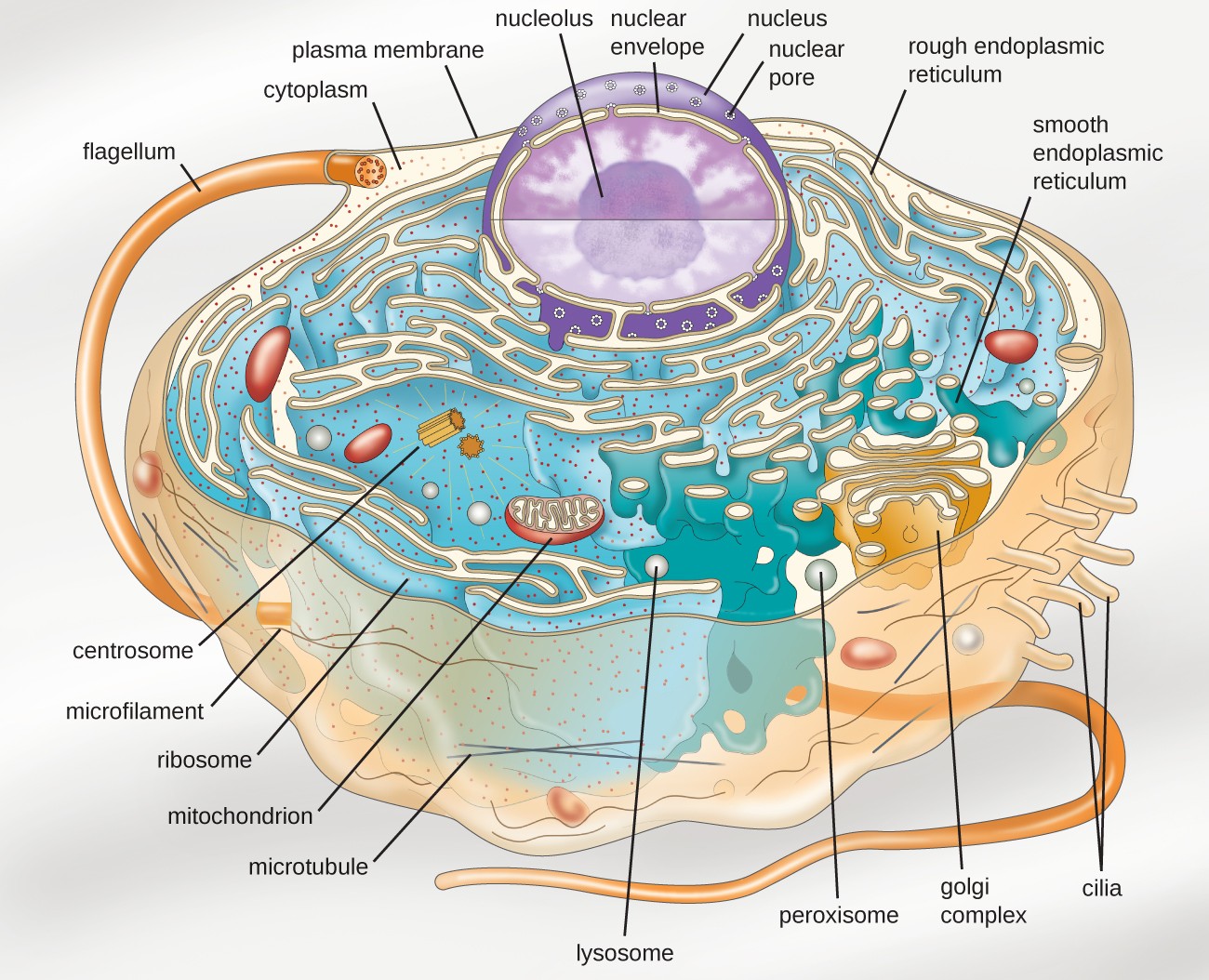
One of these particles is labeled a. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is found in all cells and separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. Describe the structure of cell membranes.
A cell’s plasma membrane defines the boundary of the cell and determines the nature of its contact with the environment. Cell membrane with labeled educational structure scheme vector illustration. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell.
We all remember that the human body is very intricate and a method i discovered to are aware of it is via the style of human anatomy diagrams. Structure of the cell membrane. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that is semipermeable.
Cell wall a thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell. Take up the quiz below and get to see how much you understood its structure and how it helps it attain its functions. Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities.
Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. Membrane structure and function all cells have a plasma or cell membrane , which contains the cell. Hence the bacterial cell structure lacks a nucleus.
Use for everything except reselling item itself. It supports and helps maintain a cell�s shape. The phospholipids have a hydrophilic water attracting heads and two hydrophobic water repelling tails.
Cells exclude some substances, take in others, and excrete still others, all in controlled quantities. Proteins and lipids are the major components of the cell membrane. Start studying label cell membrane.
We all keep in mind that the human body is very elaborate and a technique. The figure shows a cell membrane with integral molecule, which consists of two similar parts with specific recess. Plasma membranes enclose the borders of cells, but rather than being a static bag, they.
The fluid mosaic model of cellular membranes: List 2 functions of the cell or plasma membrane. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments.
The cell membrane provides mechanical support that facilities the shape of the cell while enclosing the cell and its components from the external environment. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles while protecting the cell from its surrounding. The cell membrane regulates the transport of.
The exact mix or ratio of proteins and lipids can vary depending on the function of a specific cell. For the human cells, the nuclear materials are separated from the cytoplasm by a membrane known as the nuclear membrane. In the image depicted above, the part of the bilayer labeled a.
A cell’s plasma membrane defines the cell, outlines its borders, and determines the nature of its interaction with its environment. In a plant cell, the cell wall is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and proteins while in a fungal cell, it is composed of chitin. The major components of the cell are 1 cell membrane 2 cytoplasm and 3 nucleus.
While lipids help to give membranes their flexibility, proteins monitor and maintain. Identify components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. The formation of cell membranes is crucial to life.
The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds the cytoplasm of all prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including plant and animal cells. There are many particles in the extracellular fluid. Thin membranes bound all living cells and many of the tiny organelles internal to cells.