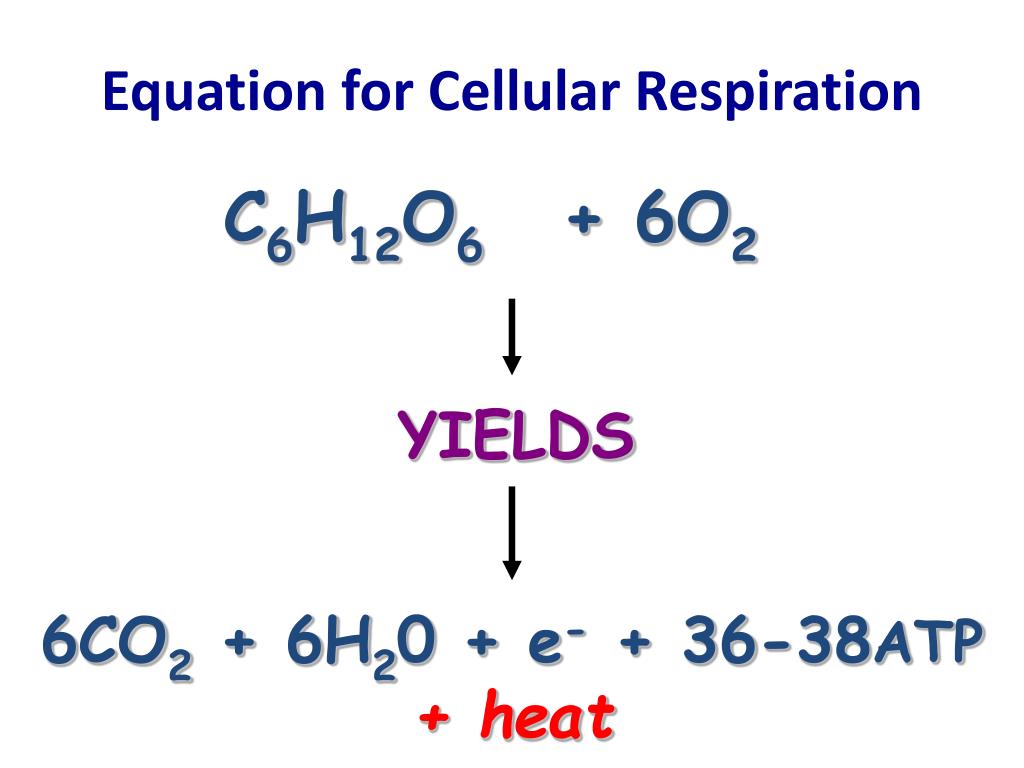
C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6o 2 6co 2 + 6h 2 o + 36 or 38 atps. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy.

Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism.
Cellular respiration formula definition. The following are general representations (formulae) for both photosynthesis and cellular respiration: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. This requires two reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide molecules (nad +) and two atp.
Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. Cellular respiration or cell respiration a catabolic process (see catabolism) occurring in cells where complex organic molecules are broken down to release energy for other cellular processes. Cellular respiration is the of photosynthesis.
C 6 h 12 o 6 (glucose)+ 6o 2 + 36 adp (depleted atp) + 36 p i (phosphate groups)→ 6co 2 + 6h 2 o + 36 atp Cellular respiration, or respiration, occurs in the. Mitochondria in aerobic respiration cytoplasm occurs while anaerobic respiration only.
Converted in the cells to energy (atp). Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. This is the balanced equation that yields energy.
The series of metabolic processes by which living cells produce energy through the. Small molecule that helps enzymes catalyze reactions. The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and adp to produce carbon dioxide, water, and atp:
To create atp and different types of electricity to strength mobile reactions, cells require gasoline and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical procedure of turning electricity right into a useable shape. All microorganisms, including individuals able to photosynthesis, feel the procedure for cellular respiration. But the last two steps, the krebs cycle and etc, happen in the mitochondria.
Cellular respiration (a three stage process) converts glucose and oxygen to atp (the cellular form of energy) and releases carbon dioxide and water. Cellular respiration helps cells break sugar which further helps in producing energy. Process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy.
During glycolysis, glucose breaks down into two pyruvate molecules. The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is: Synthesis of proteins and responses to chemical signals at the surface.
Cellular breathing is the procedure thru which cells convert sugars into electricity. The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms. Cellular respiration synonyms, cellular respiration pronunciation, cellular respiration translation, english dictionary definition of cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (atp). Glucose (sugar) + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy (as atp) aerobic cellular respiration has four stages. C 6 h 12 o 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 o 2 6 co 2 + 6 h 2 o + 36 atp (energy)
The chemical equation for aerobic respiration is glucose + oxygen gives carbon dioxide + water + energy whereas the equation for anaerobic respiration is glucose, giving lactic acid + energy. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy. Aerobic respiration is comprised of three major steps:
Definition of cellular respiration : Cellular respiration (aerobic) c6h12o6 + 6o2 → 6co2 + 6h2o + 32 atp C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6o 2 6co 2 + 6h 2 o + 36 or 38 atps.
Click to see full answer. Cell respiration usually occurs in the presence of oxygen (see aerobic respiration) but some organisms can respire without oxygen (see anaerobic respiration). Cellular respiration is a metabolic process consisting of a series of steps to convert chemical energy (sugar) into a usable form of energy (atp) in the cell.
Glucose + + o 2 glucose + + o 2 sunlight + water + + h 2 o + water + + h 2 o photosynthesis equation C6h12o6 + o2 h2o + co2. Likewise, “biological machines” also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.perhaps the second most important molecule (dna is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as atp).basically, atp serves as the main energy.
The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs, where it is exchanged for oxygen. Please label the diagram and fill in the blanks below. C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6 o 2 → 6 co 2 + 6 h 2 o + energy (as atp) the word equation for this is: