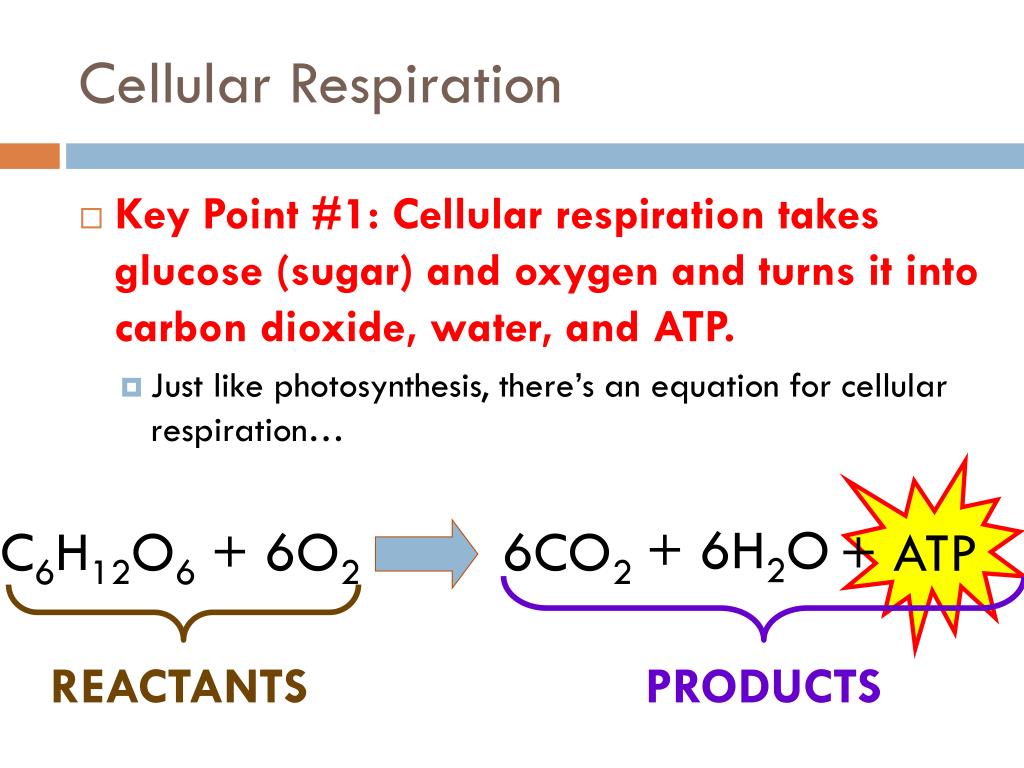
Now that we know what the reactants of cellular respiration are, let’s take a look at how they interact with one another. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as:
Usually, this process uses oxygen, and is called aerobic respiration.it has four stages known as glycolysis, link reaction, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.
Cellular respiration formula with states. To unlock this lesson you must be a. Spelled out, it states that glucose and oxygen yield carbon dioxide and water and a maximum. Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy the equation is formulated by.
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms convert the biochemical energy of nutrients into atp. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. 4 stages of cellular respiration are metabolic pathways that contribute to the production of atp molecules in cells.
Due to their multiple oxidation states, fad molecules are involved in the transfer of electrons from one molecule to another. You will measure 3 different indicators of cellular respiration: In the case of cellular respiration, the fad involved exists in two oxidation states;
In this process, each molecule of. The chemical formula that represents all of these stages throughout the cellular respiration process is: Now, the formula seems innocent, but it got me thinking.
Now that we know what the reactants of cellular respiration are, let’s take a look at how they interact with one another. Humans, animals and plants depend on the cycle of cellular respiration and. C 6 h 12 o 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 o 2 = 6 co 2 + 6 h 2 o + 36 atp (energy) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide +.
Cellular respiration helps cells break sugar which further helps in producing energy. Cellular respiration requires oxygen (which is breathed in) and creates carbon dioxide (which is breathed out). Cellular respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
What follows cellular respiration’s balanced equation/formula: C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6 o 2 → 6 co 2 + 6 h 2 o + 38atp ( glucose +. The overall chemical equation for aerobic respiration is c6h12o6 + 6o2 + 6h2o → 12h2o + 6co2 + 36/38atp.
The chemical reaction of cellular respiration is c6h12o6 + 6o2 → 6co2 + 6h2o the chemical reaction of photosynthesis is 6co2 + 6h2o → c6h12o6+ 6o2 also read: The balanced chemical equation for cellular respiration. It is symbolized by the chemical formula of c 6 h 12 o 6 6o 2 6co 2 6h 2 o c 10 h 16 n 5 o 13 p 3 also known as atp.
Cellular respiration plays an important role in releasing the energy to break down glucose to make atp (adenosine triphosphate). Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as: All organisms respire in order to release energy to fuel their living processes.
This is the balanced equation that yields energy. The respiration can be aerobic, which uses glucose and oxygen, or anaerobic which uses only. You can also search it online for more information.
Adenosine triphosphate, also knew as, atp is an organic compound, which provides energy in living cells in the body. Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as. C 6 h 12 o 6 (glucose)+ 6o 2 + 36 adp (depleted atp) + 36 p i (phosphate groups)→ 6co 2 + 6h 2 o + 36 atp
It states that c6h12o6 (glucose) + 6o2 (oxygen) creates 6co2 (carbon dioxide) + 6h2o (water). To anyone not familiar with cellular respiration, it is the chemical formula taught in schools for breathing. C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6o 2 6co 2 + 6h 2 o + 36 or 38 atps.
This lab will address how exercise (increased muscle activity) affects the rate of cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is what cells do to break up sugars to get energy they can use. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (atp).
C 6 h 12 o 6 glucose 6o 2 36 adp depleted atp 36 p i phosphate groups 6co 2 6h 2 o 36 atp. The breakdown of glucose include such cellular respiration steps as glycolysis, the transition reaction, the krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The overall unbalanced chemical equation for cellular respiration is.
To emphasize this point even more, the equation for photosynthesis is the opposite of cellular respiration. This process breaks down glucose into six carbon dioxide molecules and twelve water molecules. Anaerobic respiration the first step in cellular respiration in all living cells is glycolysis, which can take place without the presence of molecular oxygen.if oxygen is present in the cell, then the cell can subsequently take advantage of aerobic respiration via the tca cycle to produce much more usable energy in the form of atp than any anaerobic pathway.
Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. Living things make use of this energy by a process called cellular respiration. The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and adp to produce carbon dioxide, water, and atp:
You could also read the cellular respiration formula like this: Cellular respiration takes in food and uses it to create atp, a chemical which the cell uses for energy. C_6h_12o_6 + o_2 → co_2 + h_2o + energy > the balanced equation is c_6h_12o_6 + 6o_2 → 6co_2 + 6h_2o + energy the equation expressed in words would be:
Ene‑1.l.3 (ek) , ene‑1.l.4 (ek) , ene‑1.l.5 (ek) , ene‑1.l.7 (ek) cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Usually, this process uses oxygen, and is called aerobic respiration.it has four stages known as glycolysis, link reaction, the krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. In plain english, this can be read as:
The overall (unbalanced) chemical equation for cellular respiration is: Breathing rate, heart rate, and carbon dioxide production.