Cellular plants synonyms, cellular plants pronunciation, cellular plants translation, english dictionary definition of cellular plants. Types of respiration in plants.
Unlike animals, plants do not have a special organ for the exchange of gases except lenticels and stomata.
Cellular respiration in plants definition. It occurs in the presence of atmospheric oxygen. Aerobic respiration is more efficient and can be utilized in the presence of. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy.
Cellular respiration in plants photosynthesis in plants. Cellular respiration in plants process. A plant uses oxygen for oxidizing high.
Identify the similarities and differences in the. The respiration process in plants occurs using various respiratory substrates, while the most common being glucose. Plant respiration is the process of plants using up the sugars made through photosynthesis and turning them into energy for growth, reproduction, and other life processes.
The respiration process in plants occurs using various respiratory substrates, the most common being glucose. Definition of cellular respiration : They use their cellular respiration technique to survive.
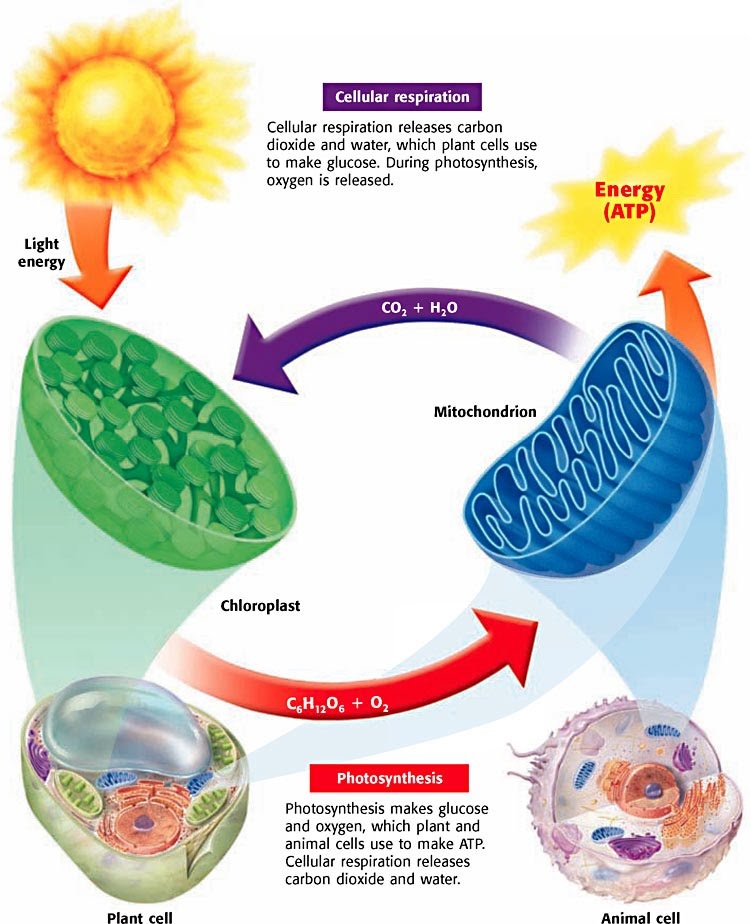
Respiration is the most vital, cellular, enzymatically controlled, catabolic process, which involves the liberation of energy by the breakdown of food substances inside the living cells. Cellular respiration (a three stage process) converts glucose and oxygen to atp (the cellular form of energy) and releases carbon dioxide and water. Plants create their own energy through photosynthesis and also use cellular respiration to produce atp.
Those flowerless plants which have no ducts or fiber in their tissue, as mosses, fungi, lichens, and algæ. Unlike animals, plants do not have a special organ for the exchange of gases except lenticels and stomata. In this process glucose is broken down in the presence of molecular oxygen into six molecules of carbon dioxide, and much of the energy released is preserved by turning adp and free phosphate into atp.
In cellular respiration, glucose first oxidizes into pyruvate by a series of enzymes. Types of respiration in plants. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients.
Cellular respiration is the process by which cells get their energy in the form of atp. In horticulture cellular respiration is the conversion of nutrients into usable energy and a release of the waste byproducts such as. The process of cell catabolism in which cells turn food into usable energy in the form of atp.
It’s also possible to export it to other cells within the organism. Cellular respiration is the process by which mitochondria is used to convert the energy in food to atp. The glucose made in photosynthesis travels around the plant as soluble sugars and gives energy.
Cellular respiration is the process of converting chemical energy into adenosine triphosphate (atp), which occurs in plants as well as animals. In this process of cellular respiration, plants generate glucose molecules through photosynthesis by capturing energy from sunlight and converting it into glucose. Cellular plants synonyms, cellular plants pronunciation, cellular plants translation, english dictionary definition of cellular plants.
By the blend of water and minerals with sunlight and c[o.sub.2], green plants form link between earth and sky. Plants breathe differently than human beings. Plants make their own food by photosynthesis.
To create atp and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form. During photosynthesis a plant takes in water,. Converted in the cells to energy (atp).
The process of cellular respiration takes control at this point. Plants take part in respiration all through their life as the plant cell needs the energy to survive, however, plants breathe differently, through a process known as cellular respiration. There are two types of cellular respiration, aerobic and anaerobic.
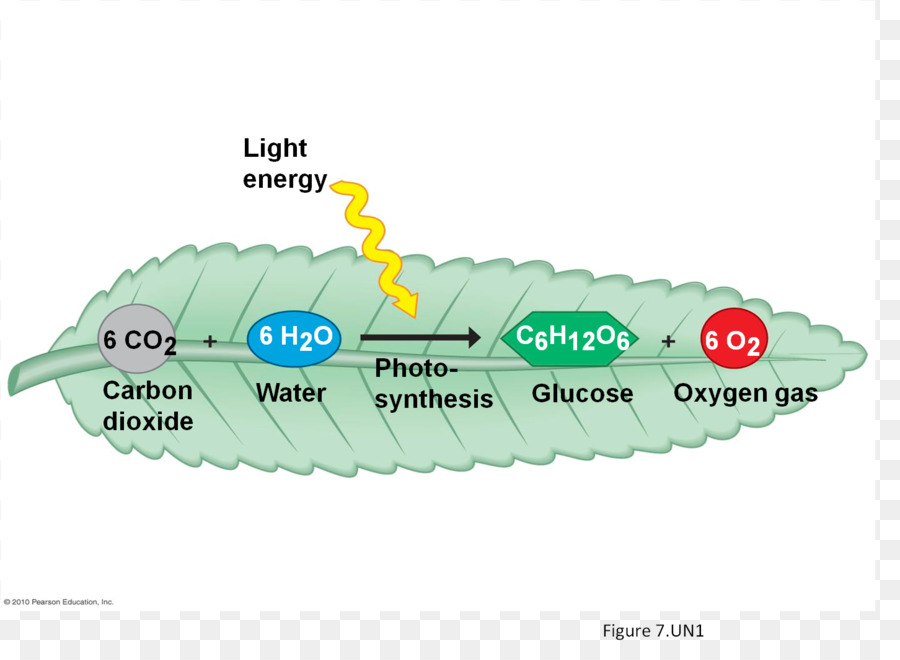
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars, such as glucose, and oxygen in the presence of sunlight. They create glucose by photosynthesis and use that energy during the respiration process. Cellular respiration involves the breakdown of glucose and the storage of the energy received into the molecule atp.
The chloroplasts produce glucose, which may then be utilized to fuel other processes inside the cell. Living, active, or occurring in the absence of free oxygen. Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic reactions that occur within the cells of organisms (both plants and animals) to convert biochemical energy derived from nutrients to adenosine triphosphate (atp) and then release waste products.
Four separate pathways drive the production of atp during cellular respiration. Breathing is one process in respiration. Respiration is the most vital, cellular, enzymatically controlled, catabolic process, which involves the liberation of energy by the breakdown of food substances inside the living cells.
C 6 h 12 o 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 o 2 6 co 2 + 6 h 2 o + 36 atp (energy) Here solar energy is converted into chemical energy and encapsulated in organic substances, while oxygen is released in air to be taken up again by other plants and by animals in the process of cellular respiration. As plants breathe normally at night, it is not recommended to sit below plants to avert carbon dioxide reach the air.
Process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy.