Receives electrons from this process begins by converting 1 molecule of 10 22 enters the matrix if oxygen is present in the cell. It is the process by which organisms use energy from “food” (e.g., glucose, fatty acids) to fuel the endergonic synthesis of atp.

Occurs in the inner mitochondrial matrix the acetyl group detaches from the.
Cellular respiration process summary. Glycolysis, which occurs in the cytoplasm. Well, it is glucose and oxygen combined together to form carbon dioxide and water. Receives electrons from this process begins by converting 1 molecule of 10 22 enters the matrix if oxygen is present in the cell.
It does not occur at any set time or at the same point in time. Respiration describes the mechanism by which cells break down food into usable cellular energy. Cellular respiration is a catabolic reaction taking place in the cells.
Summary of cellular respiration 1. Glycolysis, the krebs cycle, and electron transport. Food is the fuel for respiration.
The breakdown of organic molecules to produce atp is known as cellular respiration. An overview of cellular respiration glucose and other molecules from food are broken down to release energy in a complex series of chemical reactions that together are called cellular respiration. The exhaust is carbon dioxide and water.
Converted in the cells to energy (atp). Citric acid or tca cycle: Atp is the key molecule in this process, where it acts as a currency for cellular energy.
Cellular respiration is the process by which living cells break down glucose molecules and release energy. The pathway involves redox reactions that move electrons between molecules and energy transfer. The process is similar to burning, although it doesn’t produce light or intense heat as a campfire does.
Occurs in the inner mitochondrial matrix the acetyl group detaches from the. C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6o 2 → 6co 2 + 6h 2 o. Organic compounds + o2 à co2 + h2o + energy (atp + heat).
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces atp. Cellular respiration is the process in which cells break down glucose, release the stored energy, and use it to make atp. To create atp and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form.
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process that rearranges atoms in molecules of food through multiple steps to ensure that stored food is available to cells. Glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the kreb’s cycle and the electron transport chain. C6h12o6 + 02 6co2 + 6h2o + energy + heat intermediates 2 step 1 step 2 step 3 step 4 the breakdown of pyruvate 14 zo the e.t.
The main steps involved in cellular respiration are. Describe the summary equation for. This pathway is anaerobic and takes place in the.
This produces a net gain of two atp and two nadh molecules for the cell. The overall chemical reaction for cellular respiration is one molecule of glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) and six molecules of oxygen (o 2) yields six molecules of carbon dioxide (co 2) and six molecules of water (h 2 o). Cellular respiration (a three stage process) converts glucose and oxygen to atp (the cellular form of energy) and releases carbon dioxide and water.
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. It is the process by which organisms use energy from “food” (e.g., glucose, fatty acids) to fuel the endergonic synthesis of atp. In aerobic respiration, oxygen is required.
• requires (o 2), occurs in most organisms (plants, too!) • provides a supply of usable energy for cells (atp) c 6 h 12 o 6 6hco 2 2 oatps glucose oxygen gas carbon dioxide 6 water energy +o 2 + 6 c 6 h 12 o Respiration consists of 4 steps: Cellular respiration summary cellular respiration is the enzymatic breakdown of glucose (c6h12o6) in the presence.
The process begins in the cytoplasm and is completed in a mitochondrion. Citric acid cycle or krebs cycle, which occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. Cellular respiration is similar in broad principle to the combustion of gasoline in an automobile engine after oxygen is mixed with hydrocarbon fuel.
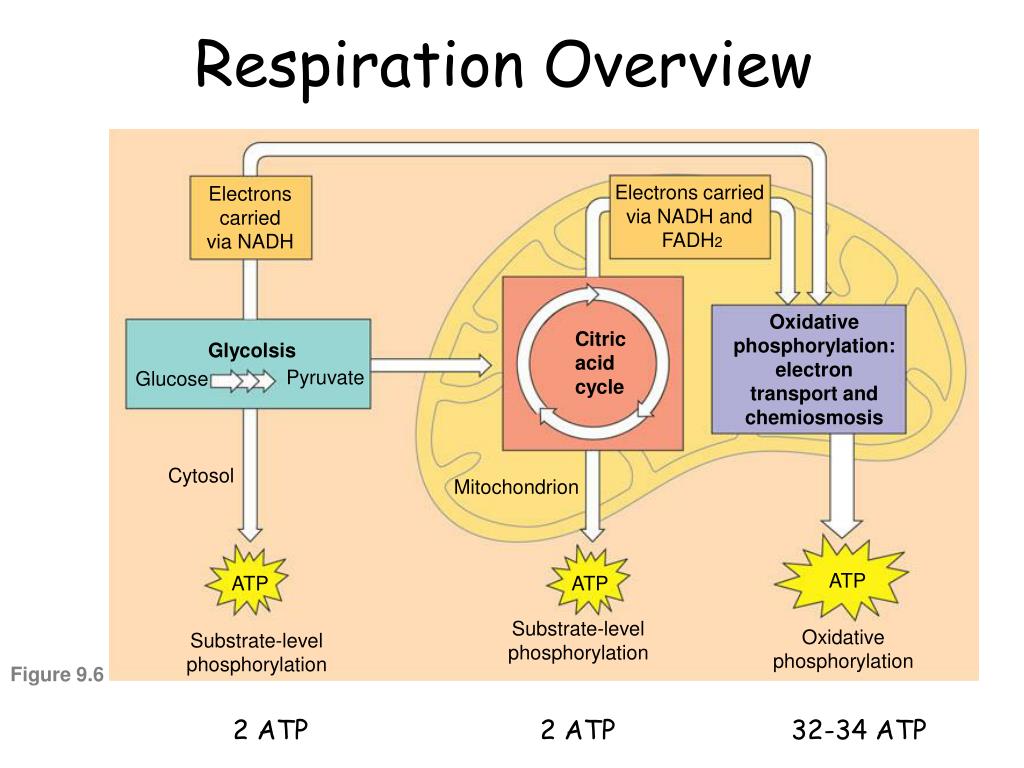
In fact, neighboring cells are simultaneously involved in different stages of cellular respiration. What is the summary equation of cellular respiration? The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid or krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
Glycolysis is the first pathway in cellular respiration. Process that does not use oxygen. C 6 h 12 o 6 + 6o 2 ® 6 co 2 + 6h 2 o + 38 atp.
It is linked to mitochondrial ros production and detoxification, generation of electrochemical gradients across membranes, thermogenesis, and oxidative phosphorylation. This is because cellular respiration releases the energy in glucose slowly, in many small steps. Mar 23, 2018 the full chemical equation is:
In eukaryotes, pyruvate oxidation takes place in the mitochondria. C 6 h 12 o 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 o 2 6 co 2 + 6 h 2 o + 36 atp (energy) Using chemical symbols the equation is represented as follows:
There are two types of cellular respiration: It is a biochemical process by which nutrients are broken down to release energy, which gets stored in the form of atp, and waste products are released. Cellular respiration is carried out by every cell in both plants and animals and is essential for daily living.
Cellular respiration occurs in three stages: Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into atp, and then release. Biology energy in organisms fermentation / anaerobic respiration.
Process in which organisms convert energy in the presence of oxygen. Cellular respiration is an exergonic reaction, which means it Cellular respiration is the enzymatic breakdown of glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) in the presence of oxygen (o 2) to produce cellular energy (atp):