Fennec fox (vulpes zerda) 2. Dromedary camel (camelus dromedarius) 4.

Desert plants and animals display a fascinating variety of adaptations that help them thrive here.
Desert animal adaptations list. Examples of desert animals include grasshoppers snakes kangaroo rats coyotes and bald eagles. Desert animals must adapt to harsh conditions in order to survive. Some animals move around so that they have the least contact with the burning sand as possible, such as the sidewinder.
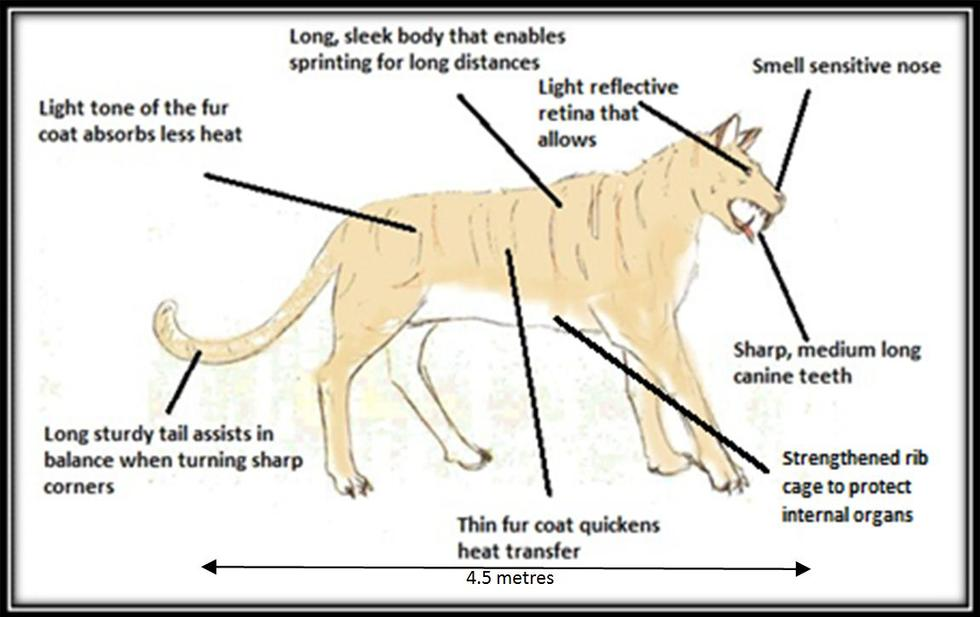
Desert tortoises have an oversized bladder that can carry extra water. Hairy paws for walking on hot sand; The main task of the lesson involves pupils creating their own animal suited to a desert, they can choose features from the handout (make sure they reflect a desert environment).
N octurnal desert animals keep cool by being active at night, whereas some other desert animals get away from the sun’s heat by digging underground burrows. Fennec fox (vulpes zerda) 2. They burrow under the sand to protect themselves from the intense heat in the summer and subfreezing temperatures while it is dormant in the winter.
Whether these adaptations help them hide, scare predators away or even taste bad depends on each animal’s traits and environment. And living in a burrow. Some animals keep themselves cool by having large ears, such as the jackrabbit or the kit fox.
This google slides digital resource with 17 slides provides practice for students to research animal adaptations in the As you can see from the climate graph for kuwait, plants and animals in the desert have to cope with very little water. What animal has adapted to survive in the australian desert.
Their low body fat percentage, coupled with their naturally low body temperature means armadillos face the possibility of death in colder environments. Desert plants and animals display a fascinating variety of adaptations that help them thrive here. Xerocoles are animals which adapt themselves to desert conditions.
A common desert adaptation in animals is to save water by not exposing themselves to hot temperatures. These creatures are omnivores eating seeds bulbs fungi spiders worms and insects. Plant and animal adaptations in the desert.
Becoming nocturnal and burrowing help small mammals like the bilby to survive the hot and dusty days. Up to 24% cash back desert elephants. Desert tortoises are active mostly during the day depending on the temperature.
Leopard gecko (eublepharis macularius) 3. Semidesert habitats have enough rainfall to support more plant and animal life. • copy of desert animal list • strips of paper • bowl to hold strips of paper • copy of desert adaptation teacher�s guide on pages 5 to 11 • internet or library access • water desert animal list 1.
These animals can be classified as drought resistors and drought evaders. They also love to dig burrows to bury themselves in and spend most of their day sleeping, making the desert sands their ideal napping spot. Dromedary camel (camelus dromedarius) 4.
The desert animal adaptations interactive digital notebook is designed to support the next generation standards for learning about adaptations in third grade (ls3.a, ls3.b, ls4.c). Their large ears release large amounts of heat through veins, keeping the rest of their body cooler. Examine desert plants’ structures to reveal how they deal with the temperature extremes and aridity of this environment.
Tropical rainforests, because of their location near the equator, cover only a small area on our planet.interestingly,. Large ears for dissipating body heat; The following files are pdf files.
The ability either to store water or to survive on very little water; They excrete a dry metabolic waste product in the form of uric acid and guanine so that water loss is minimal. Then meet some live desert animals and identify their secrets to success as desert dwellers.
One stomach stores food and the other digests it. Explore desert animal adaptions such as burrowing during the day and becoming active at night, as well as physical adaptations. The desert tortoise has made many adaptations to its home environment.
Hummingbird bills are long and slender for probing flowers for nectar. Insects, other invertebrates, rodents, toads, desert tortoises and kit foxes use underground burrows to shelter from surface temperatures that can reach 71. Time permitting, choose pupils to show their work to others, they must be able to discuss how.
Descending from terrestrial plants, seagrasses have evolved adaptations to survive in marine environments.